JavaScript Async and Defer
JavaScript brings life to webpages, but how we load scripts matters for optimal performance. We can think of async and defer as two ways JavaScript can load and execute scripts on a webpage without blocking other processes like loading content or rendering the page.

Async
When you add the async attribute to a <script> element, it allows the browser to download the script in parallel with the loading of the rest of the webpage. As the script finishes downloading, the browser can execute it immediately, without waiting for the entire page to finish parsing. This means the script execution could happen at any time and does not block the page’s parsing process. The async attribute is beneficial for scripts that are independent of other scripts and page content since their loading does not disrupt the user’s browsing experience.

However, because async scripts do not block parsing and can be executed out of order, they are not guaranteed to run in the order they appear in the HTML. Consequently, async is best used for scripts that do not depend on other scripts and do not modify the DOM structure.
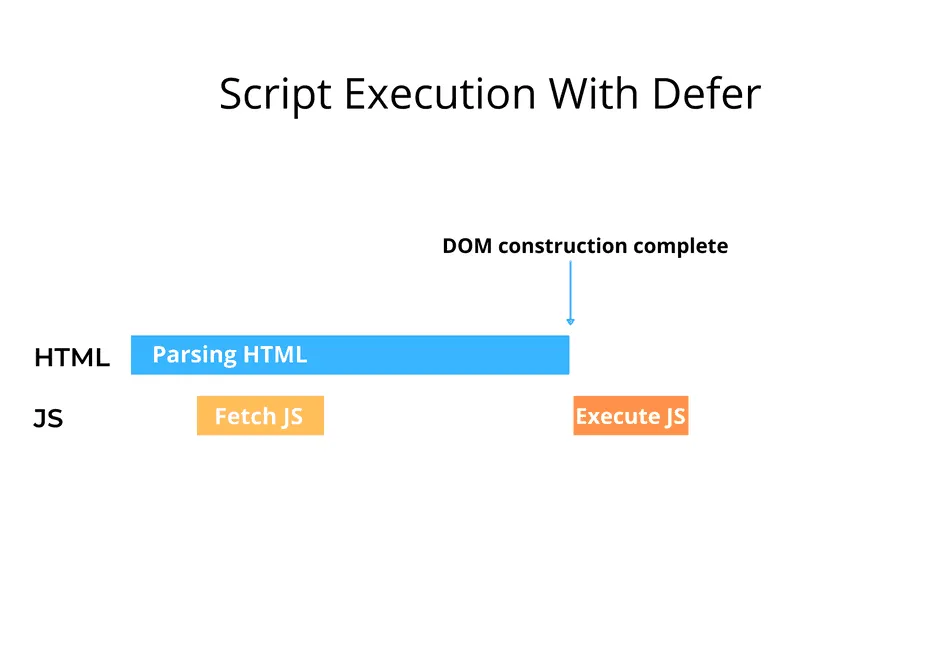
Defer
The defer attribute is used in HTML to indicate that a <script> tag should not block the loading of the page’s content. When you include defer in a <script> tag, the browser is instructed to download the script in the background while it continues to parse the HTML document. The script execution is deferred until after the HTML document has been fully parsed, ensuring that the page’s content can be displayed to the user without waiting for the script to load and execute.
Can Both Be Used Together?
While both async and defer are useful for non-blocking script loading, they should not be used together on the same script tag. If both are present, the browser will prioritize async.
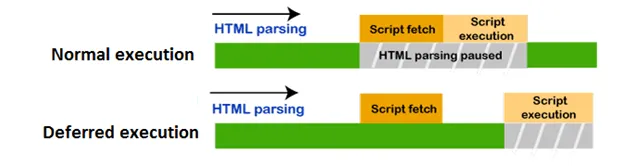
When to Use Async and When to Use Defer
Choosing between async and defer depends on your use case. Use async for independent scripts and defer for scripts that depend on other scripts or interact with the DOM.
Async Examples
- Loading tracking scripts like Google Analytics.
- Third-party widgets such as social media buttons or comment sections.
- Independent modules that operate separately from the main page content.
Defer Examples
- Manipulating or interacting with DOM elements.
- Website initialization code.
- Loading libraries or frameworks like jQuery.
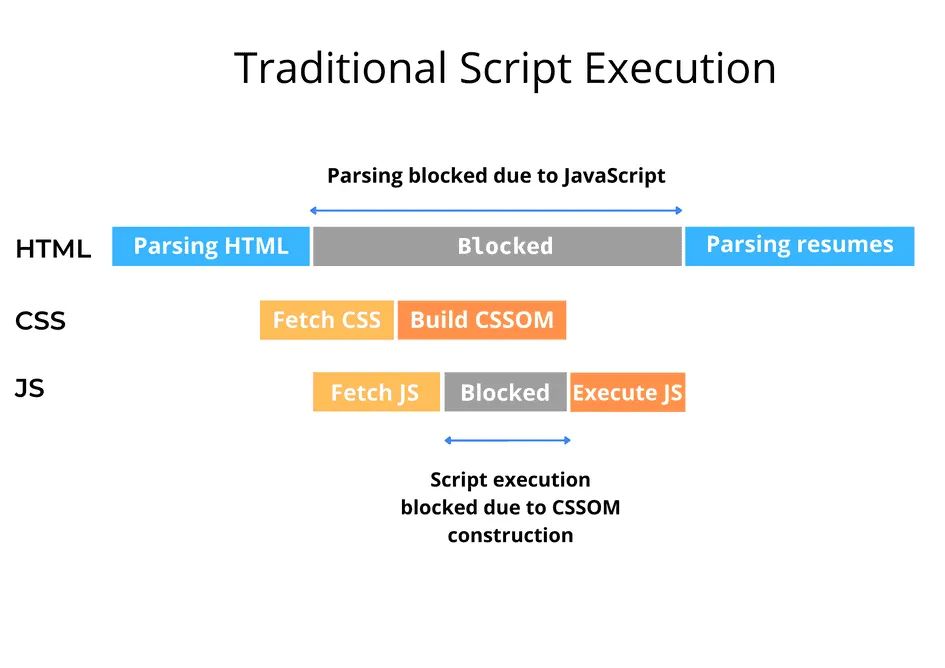
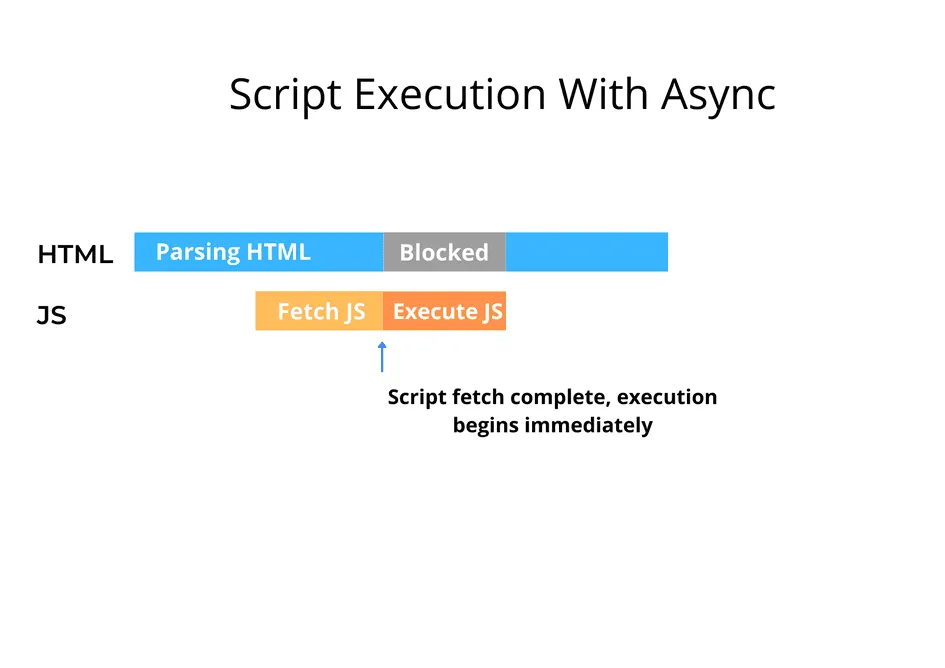
Impact on Web Performance
The choice between async and defer can significantly impact the loading time and user experience of a webpage. Use async for scripts that don’t affect initial rendering and defer for scripts that modify the DOM.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of using async and defer attributes in JavaScript is key to optimizing web performance. Understanding when to use each can make a noticeable difference in page load times and user experience.